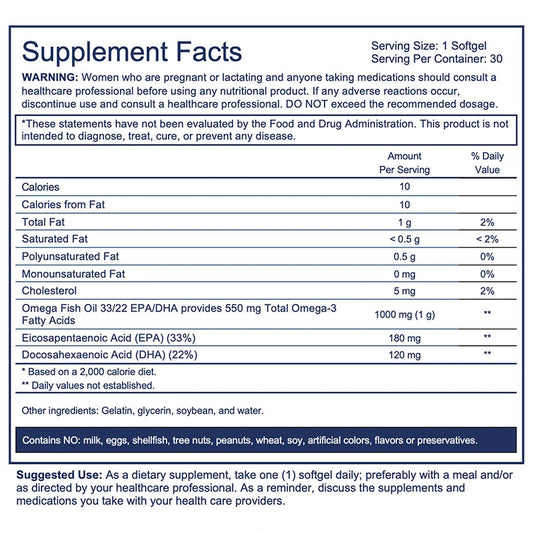
Fish oil is a dietary resource of omega-3 fatty acids — substances your body requires for many functions, from muscle activity to cell growth.
Omega-3 fatty acids are stemmed from food. They cannot be produced in the body. Fish oil contains two omega-3s called docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Dietary sources of DHA and EPA are fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel and trout, and shellfish, such as mussels, oysters, and crabs. Some nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils contain another omega-3 called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
Fish oil supplements come in liquid, capsule, and pill form.
People take fish oil to lessen the risk of heart attacks* and strokes*, to treat high triglycerides* and high blood pressure*, and to improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis*.
Research on the use of fish oil for specific conditions shows:
- Heart disease*. Studies show that consuming dietary sources of fish oil — such as tuna or salmon — twice a week is associated with a reduced risk of developing heart disease*. Taking fish oil supplements for at least six months may help to reduce the risk of heart-related events (such as heart attack). Research also suggests that the risk of congestive heart failure* is lower in older adults who have higher levels of EPA fatty acids.
- High blood pressure*. Multiple research reports limited reductions in blood pressure* in people who take fish oil supplements. There is some evidence that this effect is greater for people with moderate to severe hypertension than those with mild hypertension.
- High triglycerides and cholesterol*. There are some studies that show that omega-3 fatty acids may be able to considerably lessen blood triglyceride levels. There also appears to be a slight improvement in high-density lipoprotein (HDL, or "good") cholesterol, although an increase in levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or "bad") cholesterol also was observed.
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for good health. Try to get them from your diet by eating fish — broiled or baked, not fried. Fish oil supplements might be beneficial if you have cardiovascular disease* or an autoimmune disorder*. Fish oil also appears to contain almost no mercury, which can be a cause for concern in certain types of fish. While largely safe, too much fish oil can increase your risk of bleeding and might suppress your immune response. Take fish oil supplements under a doctor's supervision.
When taken as recommended, fish oil supplements are generally considered safe.